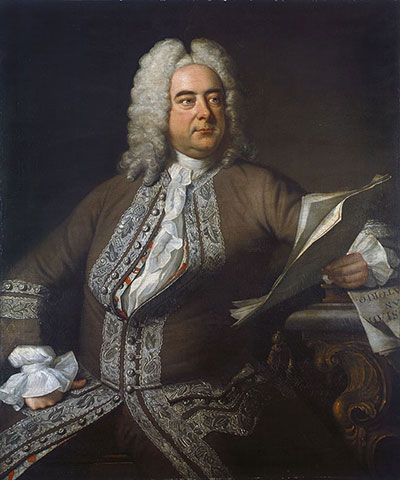
Each Advent, many churches and community choirs host the beloved tradition of a “Messiah” sing-a-long. The libretto – or text – is full of paraphrased Old Testament references to the birth of Christ and prepares listeners for a Christmas mindset.
Each Advent, many churches and community choirs host the beloved tradition of a “Messiah” sing-a-long. The libretto – or text – is full of paraphrased Old Testament references to the birth of Christ and prepares listeners for a Christmas mindset.
Although G.F. Handel’s “Messiah” is undoubtedly the most well-known oratorio in history and hugely popular in England and Germany, the genre actually originated in Italy. During the Counter Reformation, St. Philip Neri (1515-95), who wrote the rule for the Congregation of the Oratory, believed the faithful could benefit from prayers, songs, and even concerts of sacred music in the vernacular. An oratory is where such practices were held and where the word “oratorio” originates.
Initially, the genre of oratorio was small and, at times, used as a substitute for bombastic opera during the penitential season of Lent. To reflect the spirit of the season, the texts retold stories of sacrifice from the Old Testament. In the oratorio’s origins, the texts were either in Latin or the vernacular (and thus classified as oratorio latino or volgare, respectively). By the time of Handel’s “Messiah,” the length, instrumental and vocal resources had expanded monumentally, and the texts were in the language of the people.
The work was composed extraordinarily quickly: begun Aug. 22, 1741, and completed less than a month later on Sept. 14. To conserve space at the premiere, women were advised not to wear hoops in their gowns and men were asked to leave their swords at home.
“The Messiah” is in three parts, with the first part being the Christmas section. Unusual for the genre, no specific named characters appear in this part. For instance, there is no role for the Blessed Mother or St. Joseph. Instead, Charles Jennens, who also provided Handel with the text for several other oratorios, paraphrased parts of the Bible to narrate the story.
“Rejoice Greatly,” a soprano solo, is a Da Capo Aria, a three-part form with texts truncated from the Book of Zechariah (Zech 9:9-10): “Rejoice greatly, O daughter of Zion! Shout, O daughter of Jerusalem, behold thy King cometh unto thee. He is the righteous Savior, and He shall speak peace unto the heathen.” The first section begins in B-flat major, a tonality associated with hope, clearly appropriate here.
An instrumental theme opens the work and introduces the melody that will be repeated upon the soprano’s entrance. The singer repeats the word “rejoice” numerous times in the first section, with Handel enhancing the mood by adding many, many notes on reiterations of the word.
The second part of the aria provides musical contrast and begins on the text, “He is the Righteous Savior.” The joyful major key is replaced by minor with the volume lessened considerably. The final part returns to the opening in the original key and, although unnotated, the singer is expected to embellish or add extra notes, making the music simultaneously familiar and new.
Handel’s devotion to his craft was legendary. He once threatened to hold a soprano out the window until she agreed to perform the music the way he intended (she wisely acquiesced). His high standards and unwillingness to compromise contributed substantially to the history of music. His works in the sacred genre, particularly his beloved
“Messiah,” are a wonderful soundtrack to celebrate the Feast of the Nativity and prepare our hearts and minds for the coming of Our Savior.
Christina L. Reitz, Ph.D., is a professor of music at Western Carolina University in Cullowhee.
Watch it online
Watch a rendition of Handel’s “Messiah” by the Staatskapelle Dresden, conducted by Alondra de la Parra in 2019.
 Each summer, orchestras and bands across the United States provide outdoor concerts that are quite popular amid the festivities of Independence Day. Curiously, one of the works featured frequently is the “1812 Overture” by Pyotr Il’yich Tchaikovsky. The bizarre tradition of including this quintessential Russian work on American patriotic concerts stems from the early 1970s in Boston.
Each summer, orchestras and bands across the United States provide outdoor concerts that are quite popular amid the festivities of Independence Day. Curiously, one of the works featured frequently is the “1812 Overture” by Pyotr Il’yich Tchaikovsky. The bizarre tradition of including this quintessential Russian work on American patriotic concerts stems from the early 1970s in Boston.
The overture’s scoring of church bells and cannon fire were believed to complement the subsequent fireworks and increase audience attendance. It has no connection to America’s War of 1812, but rather commemorates Napoleon’s retreat from Moscow.
From a religious perspective, the overture quotes an Orthodox chant. Tchaikovsky, though he had struggles with religion, penned numerous, though lesser known, sacred works, such as the “Liturgy of St. John Chrysostom” (1878) and “Hymn in Honor of Saints Cyril and Methodius” (1885).
In 1880, Tchaikovsky received a commission from Nicolay Rubinstein, director of the Moscow Conservatory. The work was to be connected to the consecration of the Cathedral of Christ the Savior, which was erected to honor the Russian victory over the French army – although it was more of a victory for Mother Nature, as the harsh Moscow winters were the primary cause of the French downfall.
The overture begins with soli for the violas and celli quoting the Orthodox chant “Save us, O Lord” – the low registers coupled with a slow tempo especially enhance the gravity of the opening. As the piece moves along, it assumes a more militant sound through the scoring for tambour militaire (snare drum) before “La
Marseillaise,” the French national anthem, appears to represent the French invasion. At the risk of being churlish, it’s worth noting that the anthem had been banned by Napoleon and reinstated only in 1815 and, thus, Tchaikovsky’s use of the tune is not historically accurate. A similar factual inconvenience arises at the end of the work, where the Russian national anthem “God Save the Tsar” is heard amid the blasting cannons. This anthem was composed in 1833 – two decades after the events of 1812.
Despite the facts that the “1812 Overture” has nothing to do with the U.S. and that the national anthems incorporated were not in use (or in existence) at the time the work is meant to be set, it remains one of Tchaikovsky’s most beloved works. Part of the appeal is the use of cannons, certainly a rarity in the symphonic … canon.
Tchaikovsky did not think much of this work, and most music critics agree with his assessment. However, he did conduct it himself several times.
His most beloved compositions, “Nutcracker” and the “1812 Overture,” are not actually representative of his compositional style, which is often quite serious and brimming with great emotion. A more accurate reflection of his symphonic style is his final symphony, nicknamed the “Pathetique,” which premiered only days before the composer fell ill. He eventually died under circumstances that remain unclear and are likely never to be known.
— Christina Reitz, Ph.D., Special to the Catholic News Herald
Listen online
Listen to a performance of the “1812 Overture”